Responsive Vs Adaptive Web Design: Which Is Better?
As a fundamental question when embarking on any design journey, the choices of responsive and adaptive design, bear overarching consequences for websites. Although both methods deal with the reality that websites are often viewed on mobile device, they do differ in ways.
As such, companies must contemplate these dual design factors in relation to their own business and field. To help you get to grips with what sets adaptive and responsive web design apart, we’ll look at them both in more detail.
Firstly, how are they similar?
Well responsive sites and adaptive sites are the same in that they both change the appearance of a website based on the browser environment they are being viewed on.
How do they differ?
Responsive design offers an unchanging experience regardless of what device type people use. Responsive websites respond to the size of the browser at any given point, and regardless of what the browser width may be, the site has one layout that always changes to optimize the viewing experience.
In contrast, adaptive design detects the screen size and implements a suitable layout for it. In other words, the website is only concerned about the browser being a specific width, at which point it adapts the layout. Adaptive websites tend to be designed for 6 screen widths: 320, 480, 760, 960, 1200 and 1600.
This animation below illustrates the difference in behavior between responsive and adaptive web design:
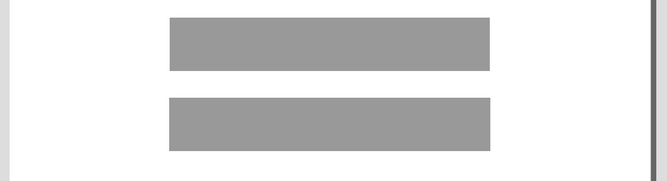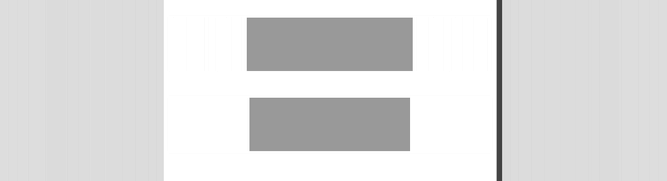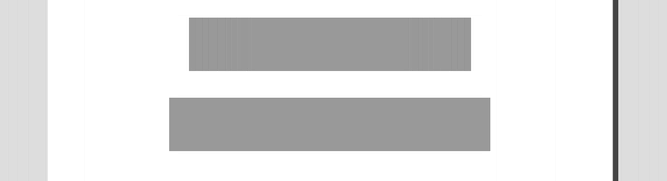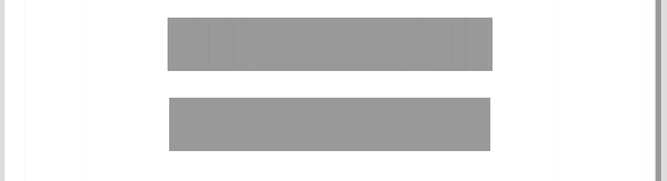
Responsive design is on top, adaptive is below. (Source: CSS Tricks)
Notice how the responsive example flows with the environment whereas the adaptive snaps into place at a defined environment.
Now, let’s look at both in more detail...
Responsive design
In an increasingly mobile society, it’s impossible to predict what device your users will view your website on. In this sense, the majority of new sites today are built to be responsive and simultaneously cater for all users.
Why responsive?
- Fluidity: All site features, including images, buttons and navigation automatically adjust to each screen size. This ensures each user has a consistent experience regardless of device type.
- Unchanging experience: Scaling content to fit a small screen is no longer enough as mobile users become predominant users. Responsive design ensures a complete and consistent experience for all site users, whether they are reading or sharing content, viewing images or clicking through various landing pages.
- Readability: A responsive site is built on a single design with very slight modifications between device types. The aim is to provide a comprehensive experience, removing the need for users to zoom and out.
- Single URL: One of the greatest benefits of responsive design is that only one URL is needed. This reduces the time needed to manage SEO.
- Lower costs: Responsive web design permits cost savings as it doesn’t necessitate rework and permits easier set up during a rebuild.
The downside:
- Responsive design certainly involves more work. An extensive amount of coding and programming is required to ensure the website pages fit every device, regardless of screen size. Focusing on providing every user with a consistent experience, responsive web design must re-assemble content so that it fluidly fits content to match the size of the device screen.
- Web page loading speed can be affected with responsive design as it’s based on a html5 structure linked to CSS styles. Mobile devices load all the data from the desktop content. Even though it only keeps 60% of it, the remaining 40% is still loaded, decreasing the site speed.
- Depending on your audience, bear in mind that web browser compatibility can be an issue, especially with older smart phones. However most newer devices will be HTML5 compatible.
Adaptive Design
Adaptive web design refers to content that is designed and built to suit various channels and media. It necessitates progressive enhancement, static layouts and device detection.
Adaptive design operates by detecting the users screen size and loading a suitable layout for it. It is often applied to existing websites to make them mobile friendly, providing the designer with greater reign over where elements are positioned on each device.
Why adaptive?
- With each device given special attention, adaptive design ensures a unique user experience. This ‘device first’ approach means that the website layout and content adapts specifically for the screen size of each device to offer users an optimum, custom-made experience.
- Only the necessary elements are transferred and displayed on mobile devices, improving page loading times. For example, high-res images will only be loaded when a high-density screen is detected, eliminating unnecessary loading times for low-quality screens.
- Pre-constructed websites don’t require alteration as the layout is already built.
The downside:
- Many developers are discouraged from adaptive web design due to the extensive work required. Advanced knowledge, time and resources are necessary to prepare, implement and test multiple page layouts. Improvements and amendments can also be time consuming. Where adaptive design has different HTML codes stored for different devices, responsive design only requires one HTML that applies CSS to change the layout for each device.
- Adaptive web design requires a team of expert developers that have the skill set to manage the complex adaptive process. This might not be feasible for smaller business with restricted budgets.
It’s no secret that mobile devices can no longer be ignored by web developers when designing websites. More and more visitors are using mobile devices such as tablets and smartphones to visit websites and as such, your site should be easy to view on a mobile device. If not optimized for mobile users, your website is losing out on potential visitors and driving less traffic to your site.
Although the responsive vs adaptive debate concludes with no definitive answer, we can agree that responsive and adaptive sites are similar in that they both change appearance based on the browser environment. Nevertheless, whilst responsive websites respond to the size of the browser by fluidly adjusting the placement of elements on a web page to best fit the available space, adaptive websites adapt to the width of the browser at specific points, based on the size and capabilities of each device.
Regardless, the decision of which design to use on your website is context specific. Think about your product or service. Ask yourself, does your site need to engage users in a specific way? What kind of user behaviour do your customers personify? What do you need to keep them informed and engaged? Only when these questions are answered will you be able to determine what option is best for you.
